Chapter 2.2
Researching standards
Navigating safety standards can be overwhelming. Understanding their structure simplifies the process, ensuring you focus only on what is essential for your project. With over 800 standards, it is crucial to identify the right ones. In this chapter we provide research tools that make this task manageable and efficient.
Navigate the rules and standards
Basic safety rules
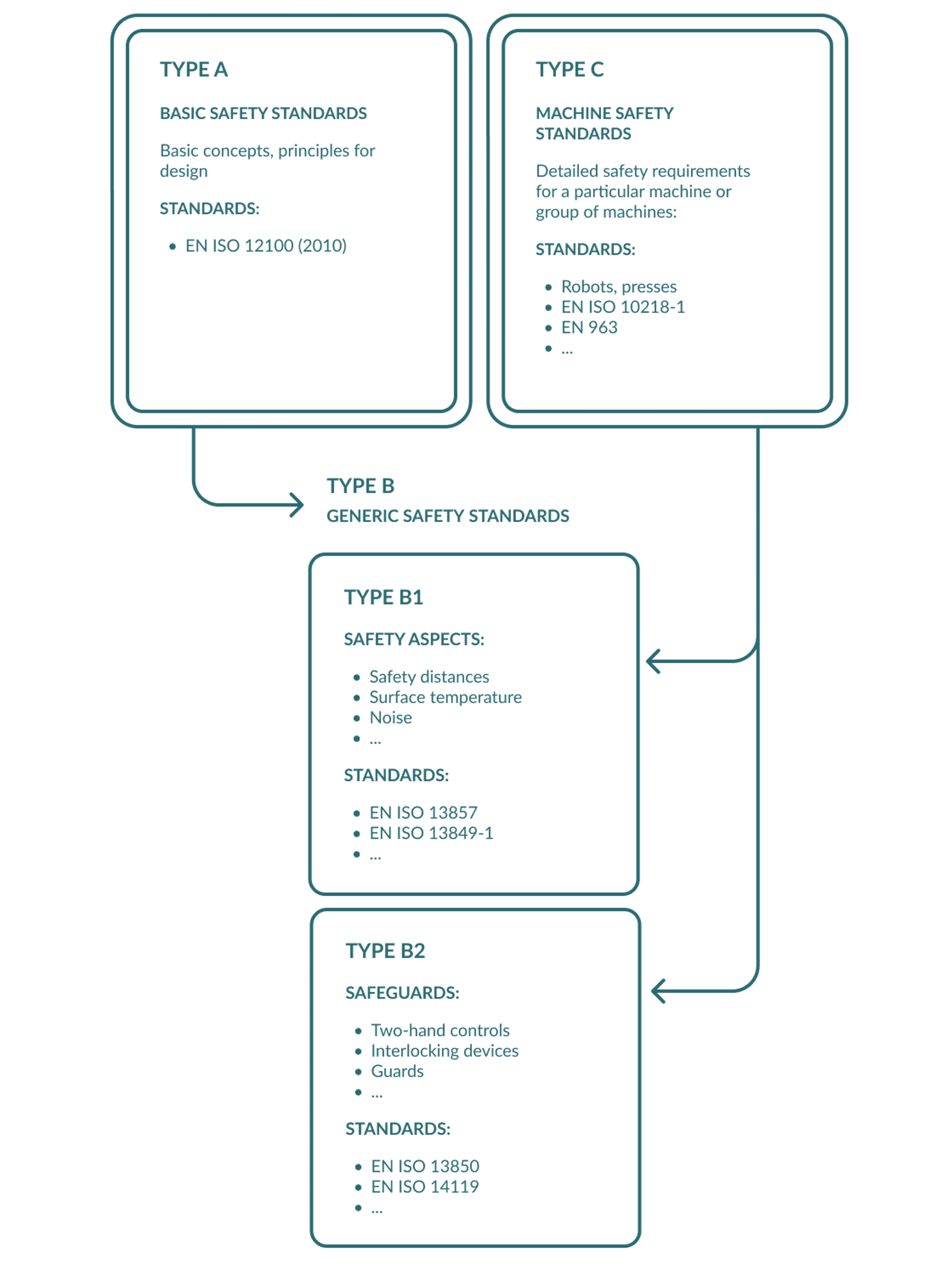
There is one A-type standard under the Machinery Directive. Then there are about 100 B-type standards with details concerning safety issues and measures. Finally, there are more than 700 C-type standards detailing machine specific safety design applicable in the EU. In all more than 800.
It might seem like an overwhelming number of standards but all of them are needed by someone, but not necessarily everyone.
The good news is: in most projects you will need to apply no more than eight to ten, but which ones? Standards research gives the answer. Although this sounds complicated and daunting, most of the information is readily available online and can be researched by anybody.
It all starts with understanding the structure of the standards program. The safety standards are arranged in a logical system allowing to research them from problem to solution. There are two alternative starting points for research (see below).
Following such research strategies will help you find the applicable requirements without having to look up a great number of standards. It also helps save needless expenditure for standards you do not really need. Axelent has prepared a chart of the B-type standards which arranges them by the type of hazard or the type of measure. It can be downloaded from our website here .

Research strategy 1
From product standard to solution details
Start with the C-type standard for the type of machine you are making; download a complete list of C-Type Standards.
You find the complete list here.
C-type standards contain a generalized risk assessment for the machine type and describe safety measures that have proven sufficient. To describe these in more detail, they may reference B-type standards.
Example: A C-type standard for machine tools like lathes (EN) ISO 23125 requires a guard with interlocking movable doors. For this safety requirement it references (EN) ISO 14120 (design of guards) and (EN) ISO 14119 (design of interlocking devices giving details on proper design of the guards.)
Research path:
- Product
- Pre-defined requirement
- Solution details
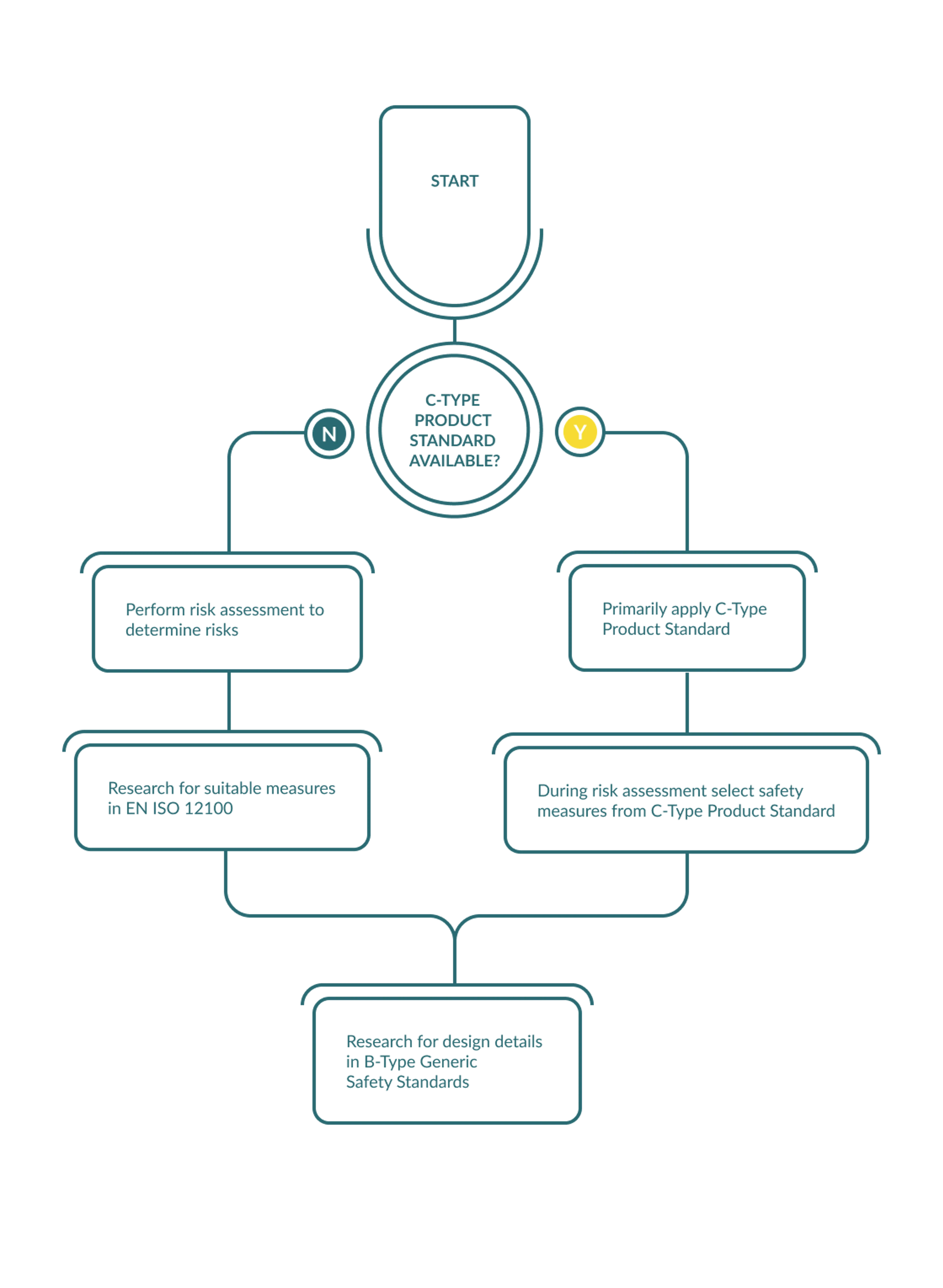
Research strategy 2
From hazard to solution alternatives
If there is no industrial safety standard for the type of machine you are making, start with the A-type standard (EN) ISO 12100 or ANSI B11.0 for the USA or CSA Z432 for Canada.
During risk assessment find the hazards and research the A-type standard for safety measures that are feasible. To describe these in more detail, the A-type standard may reference B-type standards.
Example: During risk assessment you find that hot parts may be a problem. (EN) ISO 12100 alerts you to the fact that covering or heat insulation may be required depending on the temperature. To determine the max. contact temperature allowed for certain materials it refers to (EN) ISO 13732-1, which defines admissible contact temperatures for diverse materials as well as contact times.
Research path:
- Risk identified
- Possible solution alternatives
- Solution details
